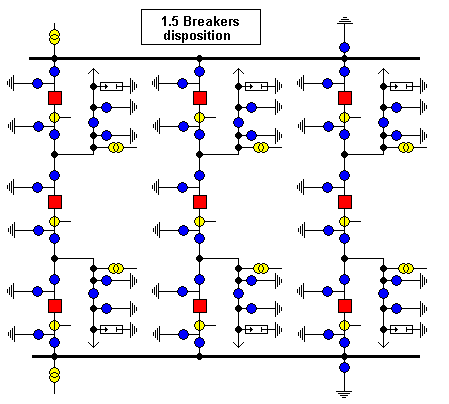
The base grid need high working safety and cheaper substations with easy expanding. Open the Modified Polygon substation, use make hybrid from two forkings, you get
the 1.5 Breakers disposition: one field has two forkings, 3 breakers ergo one forking has 1.5 breakers. That is cheaper than the Modified Poligon but it has same working safety:
All forkings have two supplies, if a busbar gets fault, the forking stays under voltage. If both busbar gets fault, the forkings stays under voltage by the central breaker independent from the substatipon.
This disposition is the best for the base grid, the switching freedom is high, in Hungary all 400 kV, big 220 kV substations have this disposition. Here can be busbar breaking too if that substation is big and important
|